Libev 源码分析 - ev_io
Libev 是使用 Reactor 模型的实现的一个高性能事件循环库。它的主要实现包括:
- 在结构上分离了事件处理逻辑和业务逻辑。
- 抽象出一套通用的多路复用接口,使得基于 Libev 编写的程序可以在不同的多路复用接口中切换(比如 Mac 上使用 kqueue,Linux 上使用 epoll),实现跨平台运行。
- 抽象 io/timer/signal 不同类型的事件,实现统一处理。
libev 的事件处理过程可以想象成如下的伪代码:
do_some_init()
while True:
t = caculate_loop_time()
deal_loop(t)
deal_with_pending_event()
do_some_clear()
首先做一些初始化操作,然后进入到循环中。 在循环中,首先计算出 waittime,然后调用 select/poll/epoll 等多路复用接口监听 fd。 如果发现有 fd 可用,就执行对应的回调函数。
主要数据类型:
-
EV_WATCHER
/* shared by all watchers */ #define EV_WATCHER(type) \\ int active; /* 表示 watcher 是否活跃,active = 1 表示还没被 stop 掉 */ \\ int pending; /* 存储 watcher 在 pendings 中的索引。大于零表示还没被处理。 * watcher 的回调函数被调用后,会设置为 0。 */ \\ int priority; /* 事件的优先级 */ \\ void *data; /* 回调函数所需要的数据 */ \\ void (*cb)(EV_P_ struct type *w, int revents); /* 回调函数 */作用:不同事件类型的共有信息。
-
EV_WATCHER_LIST
#define EV_WATCHER_LIST(type) \\ EV_WATCHER (type) \\ struct ev_watcher_list *next; /* 同一个文件描述符上可以被注册多个 watcher,比如:监听是否可读/可写 */作用:watcher 链表
-
ev_io
typedef struct ev_io { EV_WATCHER_LIST (ev_io) int fd; int events; } ev_io;作用是:记录 IO 事件的基本信息。 ev_io 相比 ev_watcher 增加了 next, fd, events 的属性。
-
ANFD
/* file descriptor info structure */ typedef struct { WL head; /* 同一个 fd 上的所有 ev_watcher 事件 */ unsigned char events; /* the events watched for,通常被设置成所有 ev_watcher->events 的或集。 */ unsigned char reify; /* flag set when this ANFD needs reification (EV_ANFD_REIFY, EV__IOFDSET) * 默认值为 0,当调用 ev_io_start 后,reify 会被设置为 `w->events & EV__IOFDSET | EV_ANFD_REIFY`。 * 如果 reify 未被设置,则把 fd 添加到 fdchanges 中去。*/ ... } ANFD;作用:
在管理 io 事件的时候,如何根据 fd 快速找到与其相关的事件,是一个需要考虑的问题。 Libev 的方法是用 anfds 数组来存所有 fd 信息的结构体,然后以 fd 值为索引直接找到对应的结构体。 -
ANPENDING
/* stores the pending event set for a given watcher */ typedef struct { W w; int events; /* the pending event set for the given watcher */ } ANPENDING;作用:存储已准备好的 watcher,等待回调函数被调用。
-
ev_loop
struct ev_loop { double ev_rt_now; /* 当前的时间戳 */ int backend; /* 采用哪种多路复用方式, e.g. SELECT/POLL/EPOLL */ int activecnt; /* total number of active events ("refcount") */ int loop_done; /* 事件循环结束的标志,signal by ev_break */ int backend_fd; /* e.g. epoll fd, created by epoll_create*/ void (*backend_modify)(EV_P_ int fd, int oev, int nev)); /* 对应 epoll_ctl */ void (*backend_poll)(EV_P_ ev_tstamp timeout)); /* 对应 epoll_wait */ void (*invoke_cb)(struct ev_loop *loop); ANFD *anfds; /* 把初始化后的 ev_io 结构体绑定在 anfds[fd].head 事件链表上,方便根据 fd 直接查找。*/ int *fdchanges; /* 存放需要 epoll 监听的 fd */ ANPENDING *pendings [NUMPRI]; /* 存放等待被调用 callback 的 watcher */ }作用:基本包含了 loop 循环所需的所有信息,为让注释更容易理解采用 epoll 进行说明。
详细可以参考:ev_vars.h 和 ev_wrap.h 文件。
执行流程:
- ev_io_init()
初始化 watcher 的 fd/events/callback。
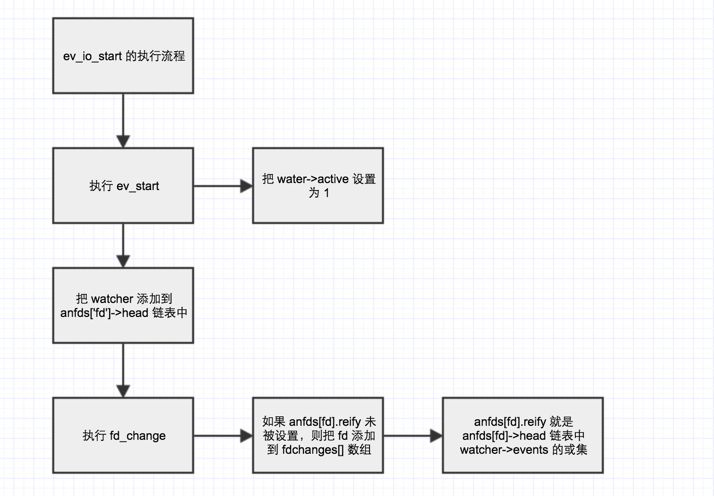
- ev_io_start()
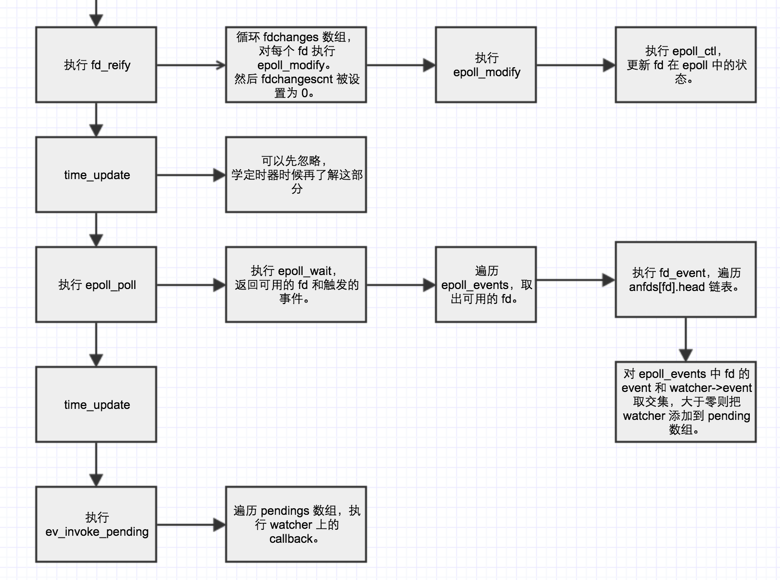
- ev_run()
几个关键数组的增/删/修改
-
loop->anfds
在管理 io 事件的时候,如何根据 fd 快速找到与其相关的事件,是一个需要考虑的问题。Libev 的方法是用 anfds 数组来存所有 fd 信息的结构体,然后以 fd 值为索引直接找到对应的结构体。
这样以 fd 为索引,anfds[fd] 中记录 fd 的相关信息。
- 增:在
ev_io_start()中,添加 watcher 到anfds[fd].head链表。 - 删:在
ev_io_stop()中,删除anfds[fd].head链表中的 watcher。 - 修改:
- anfds[fd]->active:在
ev_io_start() -> fd_change()中被修改 。 - anfds[fd]->events:在
ev_run() -> fd_reify()中被修改 ,修改为所有 watcher->events 的或集。(每循环一次就需要更新一次,因为可能有新增/删除 watcher)
- anfds[fd]->active:在
- 增:在
-
loop->fdchanges
由 fd 组成的一维数组,存储需要交给 epoll 监听的 fd。
- 增:在
ev_io_start -> fd_change中,如果发现anfds[fd]->active不为 0,即需要监听 fd 的某些事件,则添加 fd 到 fdchanges 中,fdchangescnt 加 1。 - 删:在
ev_run -> fd_reify中,遍历 fdchanges 数组,对 fd 执行epoll_modify()。遍历完 fdchanges 数组后,fdchangescnt 被设置为 0。
- 增:在
-
loop->pendings
存储待处理的 watcher,这是一个二维数组,第一个维度的索引是 priority,表示事件的优先级(普通用法不需要关注),第二个维度的索引被记录在 watcher->pending,方便定位。
- 增:在
ev_run -> epoll_poll -> fd_event中,发现有可用的 fd,则把对应的 watcher 添加到 pendings 数组,等待执行回调函数,pendingcnt 加 1。 - 删:在
ev_run -> ev_invoke_pending中,遍历 pendings,执行 watcher 上的回调函数,然后 pendingcnt 减 1。
- 增:在
Q & A:
-
Libev 是如何实现 Reactor 模型的?
需要先了解 Reactor 的 基本结构。
- Resources(资源): 对应
ev_io结构,存放事件的基本信息。 - Synchronous Event Demultiplexer(同步事件多路分用器): 对应
ev_run的实现,所有的资源都被 block 在一个大的循环中,然后通过多路复用监听所有的 fd,发现有可用的 fd 就把对应的事件存放在 pendings 中待处理。 - Dispatcher(调度器):对应
ev_invoke_pending的实现,从 pendings 取出所有待处理的事件,执行对应的回调函数。 - Request Handler(事件处理函数): 对应被注册到 watcher 上的 callback。
- Resources(资源): 对应
-
应用程序会 block 在 ev_run 吗?如果是,事件的 callback 什么时候执行?
在外部看来,程序会 block 在
ev_run。在 libev 内部,ev_run 其实是在一个大的循环中,不断取出可用的 fd,并调用对应的 callback。 -
当某个 callback 执行时间较长时候,是否会影响到其他 callback 的执行?
ev_invoke_pending从 pendings 数组中取出待执行的 watcher,并执行对应的回调函数,是同步处理的过程。如果某一个 callback 执行时间很长,会影响到其他程序。所以 callback 中尽量少执行 IO 操作。